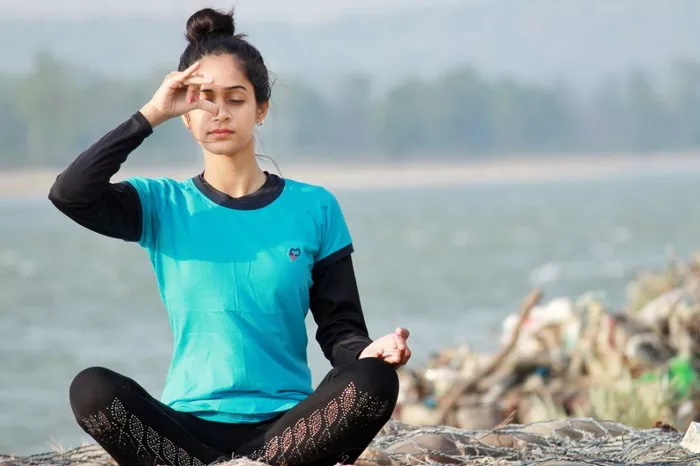
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, causing difficulty in breathing, wheezing, and coughing. While conventional medical treatments, such as inhalers and corticosteroids, remain the primary approach for managing asthma, many individuals seek complementary therapies to improve their quality of life. One such complementary therapy that has gained attention is Iyengar Yoga. This article explores whether Iyengar Yoga can effectively treat asthma, examining its principles, benefits, scientific evidence, and practical considerations.
What is Iyengar Yoga?
Iyengar Yoga is a form of Hatha yoga developed by B.K.S. Iyengar, emphasizing precision, alignment, and the use of props such as blocks, straps, and bolsters to facilitate correct postures. Unlike other yoga styles that may focus on dynamic movement or flow, Iyengar Yoga stresses holding poses for extended periods with meticulous attention to detail. This approach aims to build strength, flexibility, and body awareness gradually and safely.
Key characteristics of Iyengar Yoga include:
- Emphasis on alignment and posture accuracy.
- Use of props to assist practitioners of all levels.
- Focus on breath control (pranayama) as an integral part of practice.
- Therapeutic application to various health conditions.
Because of its therapeutic potential, Iyengar Yoga is often recommended for people with chronic illnesses, including respiratory problems like asthma.
How Does Asthma Affect the Respiratory System?
Asthma involves chronic inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which carry air in and out of the lungs. The inflammation causes swelling and narrowing, making it harder to breathe. During an asthma attack, muscles around the airways tighten (bronchospasm), mucus production increases, and airflow is restricted.
Common asthma symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath.
- Wheezing or whistling sound during breathing.
- Chest tightness or pain.
- Persistent coughing, especially at night or early morning.
The severity of asthma symptoms varies widely among individuals. While medication helps control inflammation and prevent attacks, lifestyle adjustments, including stress management and breathing exercises, may complement medical treatment.
The Role of Yoga in Respiratory Health
Yoga, as an ancient practice combining physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation, has been explored for its benefits in respiratory health. Research suggests that regular yoga practice can improve lung capacity, reduce stress, and enhance overall well-being.
Specific benefits of yoga for respiratory conditions include:
- Strengthening respiratory muscles.
- Increasing lung capacity and ventilation efficiency.
- Reducing airway inflammation through relaxation.
- Improving autonomic nervous system balance, which may lessen asthma triggers.
Among the various yoga styles, Iyengar Yoga’s focus on alignment and pranayama makes it particularly suitable for individuals with respiratory challenges.
Can Iyengar Yoga Specifically Help Asthma Patients?
Iyengar Yoga offers a structured and gentle approach to yoga, making it accessible and safe for people with asthma. The use of props allows modifications to poses, reducing strain and enhancing comfort. Moreover, Iyengar Yoga incorporates breathing techniques that can improve respiratory function.
Breathing Techniques (Pranayama)
Pranayama is the yogic practice of controlling breath, which can help regulate the respiratory system. In Iyengar Yoga, pranayama practices may include:
- Dirgha pranayama (three-part breath): Encourages deep, diaphragmatic breathing.
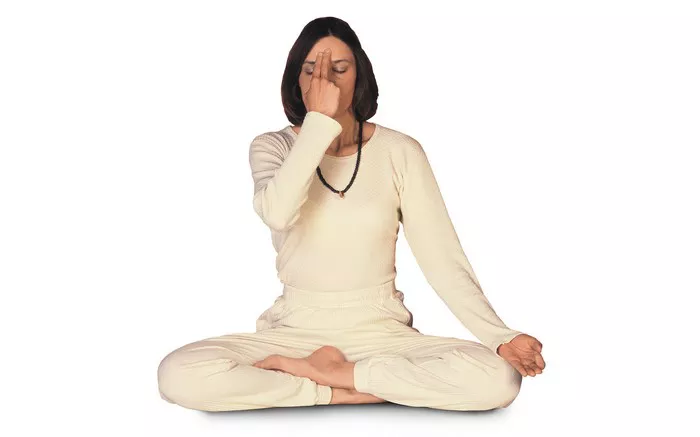
- Nadi Shodhana (alternate nostril breathing): Balances the nervous system and reduces stress.
- Ujjayi breath (victorious breath): Generates heat and promotes steady airflow.
These breathing exercises can strengthen lung function, increase oxygen intake, and calm the mind, potentially reducing asthma symptoms.
Postures Beneficial for Asthma
Certain Iyengar Yoga poses open the chest, improve posture, and expand lung capacity. These include:
- Setu Bandhasana (Bridge Pose): Opens the chest and strengthens the back muscles.
- Bhujangasana (Cobra Pose): Expands the rib cage and improves breathing.
- Tadasana (Mountain Pose) with proper alignment: Enhances posture and breathing efficiency.
- Supported backbends with props: Gently stretches the chest and lungs.
Holding these poses with attention to alignment helps reduce physical tension and facilitates easier breathing.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Iyengar Yoga for Asthma
Several clinical studies have investigated the effects of Iyengar Yoga on asthma symptoms and lung function. Although research is still developing, early results are promising.
Summary of Research Findings
- Improved Lung Function: Some studies report increases in forced expiratory volume (FEV1) and peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR) after regular Iyengar Yoga practice.
- Reduced Asthma Symptoms: Participants often experience fewer asthma attacks and reduced medication use.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Yoga practice can lower anxiety and depression linked to chronic illness.
- Better Stress Management: Since stress is a known asthma trigger, yoga’s calming effect may indirectly reduce attacks.
Limitations of Current Research
While promising, these studies often have small sample sizes, short duration, or lack control groups. Larger, well-designed randomized controlled trials are needed to confirm the therapeutic benefits of Iyengar Yoga for asthma conclusively.
Practical Considerations for Using Iyengar Yoga to Manage Asthma
If you are considering Iyengar Yoga as part of asthma management, several factors should be kept in mind.
Consult Healthcare Professionals
Always consult your healthcare provider before starting any new exercise or therapy, especially if your asthma is severe or uncontrolled.
Find a Qualified Iyengar Yoga Instructor
Look for teachers certified in Iyengar Yoga with experience in therapeutic yoga or working with respiratory conditions.
Start Slowly and Use Props
Begin with gentle postures and breathing exercises, utilizing props to ensure comfort and safety.
Monitor Your Symptoms
Track how yoga affects your asthma symptoms and medication needs. Discontinue or adjust your practice if you notice any worsening of symptoms.
Integrate with Conventional Treatment
Iyengar Yoga should complement, not replace, prescribed asthma medications and treatments.
Other Benefits of Iyengar Yoga Beyond Asthma
Practicing Iyengar Yoga can contribute to overall physical and mental health, including:
- Improved posture and musculoskeletal health.
- Increased flexibility and muscle strength.
- Enhanced mindfulness and emotional regulation.
- Better sleep quality.
- Reduced chronic pain and fatigue.
These benefits can improve general well-being, which indirectly supports asthma management.
Conclusion
Iyengar Yoga offers a structured, gentle, and therapeutic approach that may benefit individuals with asthma by improving respiratory function, reducing stress, and enhancing overall quality of life. Its emphasis on alignment, use of props, and breathing techniques make it a potentially valuable complementary therapy. However, current scientific evidence is still limited, and more rigorous research is required to establish Iyengar Yoga as a definitive treatment for asthma. Patients interested in Iyengar Yoga should consult healthcare professionals and qualified instructors, ensuring yoga practice complements standard medical care safely and effectively. Through careful integration, Iyengar Yoga can be a supportive tool in the holistic management of asthma.
Related Topics: