Thyroid disease refers to a variety of disorders that affect the thyroid gland, a small butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck. This gland plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, energy production, and overall hormonal balance by producing thyroid hormones, mainly thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). When the thyroid gland produces too much hormone, it leads to hyperthyroidism; when it produces too little, it results in hypothyroidism. Both conditions can significantly impact health, causing symptoms like weight changes, fatigue, mood fluctuations, and cardiovascular issues.
Thyroid disorders are quite common worldwide and affect millions of people. They can result from autoimmune diseases, iodine deficiency, inflammation, or even genetic predisposition. Treatment generally involves medication, lifestyle changes, and in some cases, surgery. Alongside conventional treatment, many patients seek complementary therapies such as yoga to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. One such form is Iyengar Yoga, renowned for its therapeutic approach and emphasis on alignment and precision.
What is Iyengar Yoga?
Iyengar Yoga is a style developed by B.K.S. Iyengar, focusing on detailed alignment, use of props, and holding poses for extended durations. This practice aims to enhance strength, flexibility, and balance while promoting mental clarity and relaxation. Unlike some other yoga styles that emphasize speed or flow, Iyengar Yoga prioritizes correct posture, which helps prevent injuries and makes yoga accessible to people with various physical conditions.
The use of props like blocks, straps, and bolsters allows practitioners to achieve the correct alignment even if they have physical limitations or health issues. This adaptability makes Iyengar Yoga a popular choice for therapeutic purposes, including the management of chronic illnesses. By improving circulation, stimulating the nervous system, and reducing stress, Iyengar Yoga may positively influence bodily systems involved in thyroid function.
How Iyengar Yoga May Benefit Thyroid Health
Several mechanisms suggest why Iyengar Yoga could be beneficial for people with thyroid disease:
Improved Circulation and Metabolism
Properly aligned postures can enhance blood flow to the neck region, potentially stimulating the thyroid gland. This improved circulation supports better metabolism and hormone regulation.
Stress Reduction
Chronic stress negatively affects the endocrine system, including the thyroid. Iyengar Yoga emphasizes mindful breathing and relaxation techniques, which help reduce cortisol levels and support hormonal balance.
Balancing the Nervous System
Many Iyengar Yoga poses stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system, promoting a calm state that encourages healing and homeostasis in the body, including the thyroid.
Postural Benefits
Iyengar Yoga’s focus on alignment may help correct postural imbalances that contribute to neck tension, indirectly supporting thyroid function.
Specific Iyengar Yoga Poses for Thyroid Health
Practicing targeted poses can help stimulate the thyroid gland and improve symptoms associated with thyroid dysfunction. Some commonly recommended Iyengar Yoga poses include:
Sarvangasana (Shoulder Stand)
Often called the “queen of asanas,” this pose places the thyroid gland under gentle pressure, potentially enhancing hormone production.
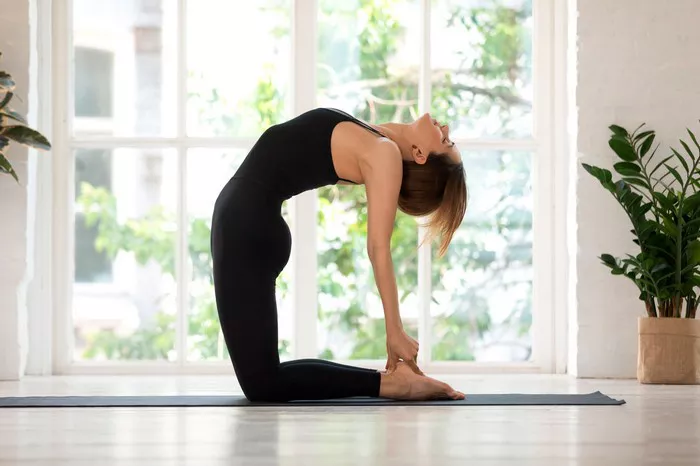
Matsyasana (Fish Pose)
This pose opens the throat and stretches the neck area, improving blood flow to the thyroid.
Halasana (Plow Pose)
This posture stimulates the neck and thyroid gland while calming the nervous system.
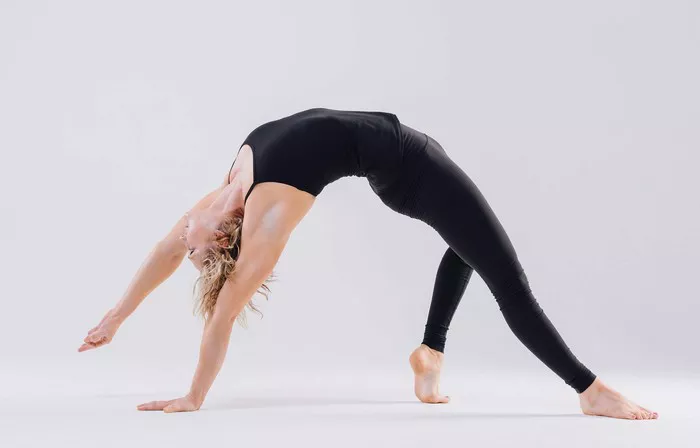
Setu Bandhasana (Bridge Pose)
This gentle backbend activates the thyroid region and supports circulation.
Each of these poses requires careful guidance, especially for people with thyroid disease, to avoid strain and ensure proper alignment. Iyengar Yoga’s use of props can be particularly helpful in safely performing these postures.
Scientific Research and Evidence on Yoga and Thyroid Disease
While scientific studies specifically focusing on Iyengar Yoga and thyroid disease are limited, broader research on yoga and thyroid health is growing. Some studies indicate that regular yoga practice can improve thyroid hormone levels, reduce symptoms, and enhance overall well-being in patients with hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
Key findings from research include:
- Yoga reduces stress hormones that negatively affect thyroid function.
- Improved autonomic nervous system balance supports hormonal regulation.
- Physical postures that stretch and compress the neck may stimulate thyroid activity.
However, more rigorous, controlled studies are needed to establish a direct causal relationship and to understand how different yoga styles, including Iyengar Yoga, may best support thyroid health.
Precautions and Considerations When Practicing Iyengar Yoga with Thyroid Disease
Despite the potential benefits, people with thyroid disorders should approach Iyengar Yoga cautiously:
- Consult Healthcare Providers: Before starting any yoga regimen, individuals should discuss it with their endocrinologist or healthcare provider.
- Qualified Instruction: Practicing under a certified Iyengar Yoga instructor ensures poses are done correctly, minimizing risks of injury or strain.
- Avoid Overexertion: Hypothyroidism can cause fatigue, so it’s essential to listen to the body and avoid pushing too hard.
- Modify Poses as Needed: Use props and modify poses to accommodate individual physical limitations or symptoms.
With these precautions, Iyengar Yoga can be a safe and supportive complementary therapy for thyroid health.
Integrating Iyengar Yoga into a Holistic Thyroid Management Plan
Thyroid disease management typically involves medication, diet, lifestyle changes, and regular medical monitoring. Iyengar Yoga can be incorporated into this plan as a supportive therapy to enhance physical and mental well-being. Some practical tips include:
- Establishing a regular Iyengar Yoga practice focused on poses that benefit the thyroid.
- Combining yoga with stress management techniques such as meditation and pranayama (breathing exercises).
- Pairing yoga with a balanced diet rich in nutrients that support thyroid health, such as iodine, selenium, and zinc.
- Monitoring symptoms and hormone levels in coordination with medical care.
This holistic approach may help improve energy levels, reduce symptoms, and contribute to a better quality of life.
Conclusion
While Iyengar Yoga cannot replace conventional medical treatments for thyroid disease, it offers promising complementary benefits. Its emphasis on alignment, use of props, and therapeutic approach make it especially suitable for individuals seeking gentle yet effective physical activity. Iyengar Yoga may help improve circulation, reduce stress, and support hormonal balance, all of which are important factors in managing thyroid health.
Ongoing scientific research will continue to clarify the extent of yoga’s benefits for thyroid disorders. Meanwhile, with appropriate guidance and medical oversight, Iyengar Yoga can be a valuable part of an integrative care strategy for those affected by thyroid disease.
Related Topics: